Haoran Sun
 |
Haoran Sun (
|
Short Bio
I was born and grew up in China. I came to the U.S. in 2015 and received my Ph.D. degree from the Department of ECE, University of Minnesota in 2021, working with Prof. Mingyi Hong. Currently, I am a Research Scientist at Facebook, Inc.
My research interests lie in machine learning and distributed optimization, with applications in wireless systems and recommendation systems.
Selected Publications
Haoran Sun, Wenqiang Pu, Xiao Fu, Tsung-Hui Chang, and Mingyi Hong, “Learning to Continuously Optimize Wireless Resource in a Dynamic Environment: A Bilevel Optimization Perspective”, Manuscript submitted for publication, available at [arXiv] [code].
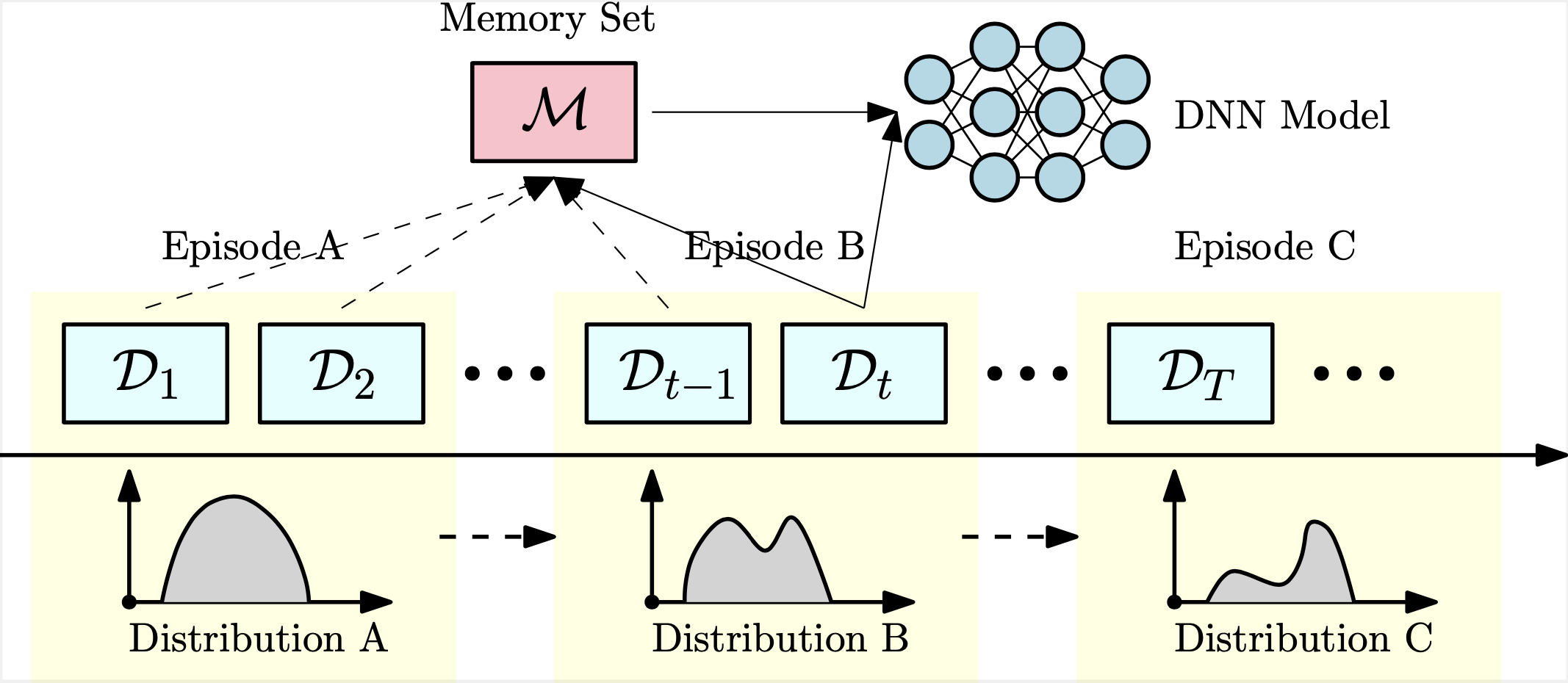 |
This work develops a methodology that enables data-driven methods to continuously learn and optimize in a dynamic environment. Our design is based on a novel bilevel formulation which ensures certain ‘‘fairness" across different data samples. Numerical results on both power control and beamforming show that the proposed CL approach is not only able to adapt to the new scenarios quickly and seamlessly, but importantly, it maintains high performance over the previously encountered scenarios as well. In the left illustration figure, the data is feeding in a sequential manner with changing episodes and distributions, and the model has a limited memory set A short version of this paper presented at the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2021. available at [IEEE Xplore] [arXiv]. |
Haoran Sun, Songtao Lu, and Mingyi Hong, “Improving the Sample and Communication Complexity for Decentralized Non-Convex Optimization: A Joint Gradient Estimation and Tracking Approach”, International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2020), available at [ICML] [arXiv] [code].
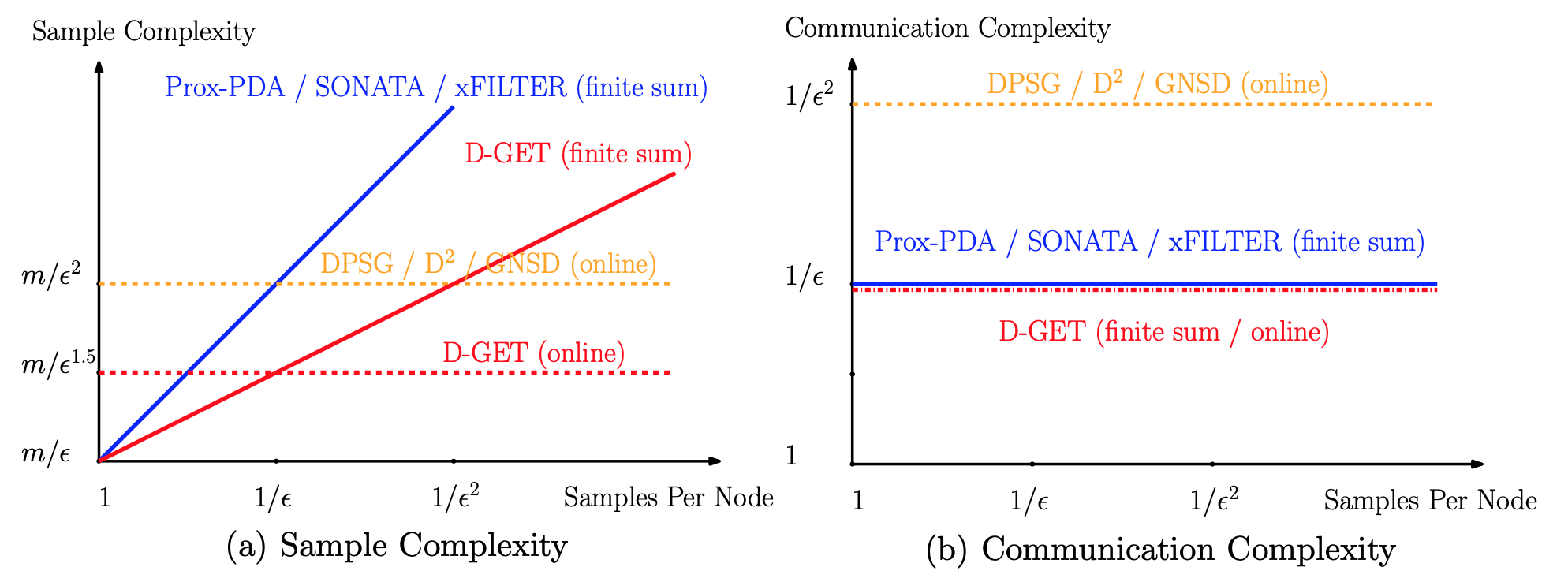 |
For a class of decentralized non-convex optimizations problems, this work aims both reducing the total communication rounds among the nodes while accessing the minimum number of local data samples. In particular, we propose an algorithm named D-GET, which jointly performs decentralized gradient estimation (which estimates the local gradient using a subset of local samples) and gradient tracking (which tracks the global full gradient using local estimates). The left figure illustrates that our D-GET algorithm significantly improves upon the best existing bounds in terms of both sample complexity and communication complexity. Note that there are m nodes in the system, and we treat the graph parameters such as eigengaps of Laplacian matrices as constants. |
Haoran Sun and Mingyi Hong, “Distributed Non-Convex First-Order Optimization and Information Processing: Lower Complexity Bounds and Rate Optimal Algorithms”, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing (2019); available at [IEEE Xplore] [arXiv] [code].
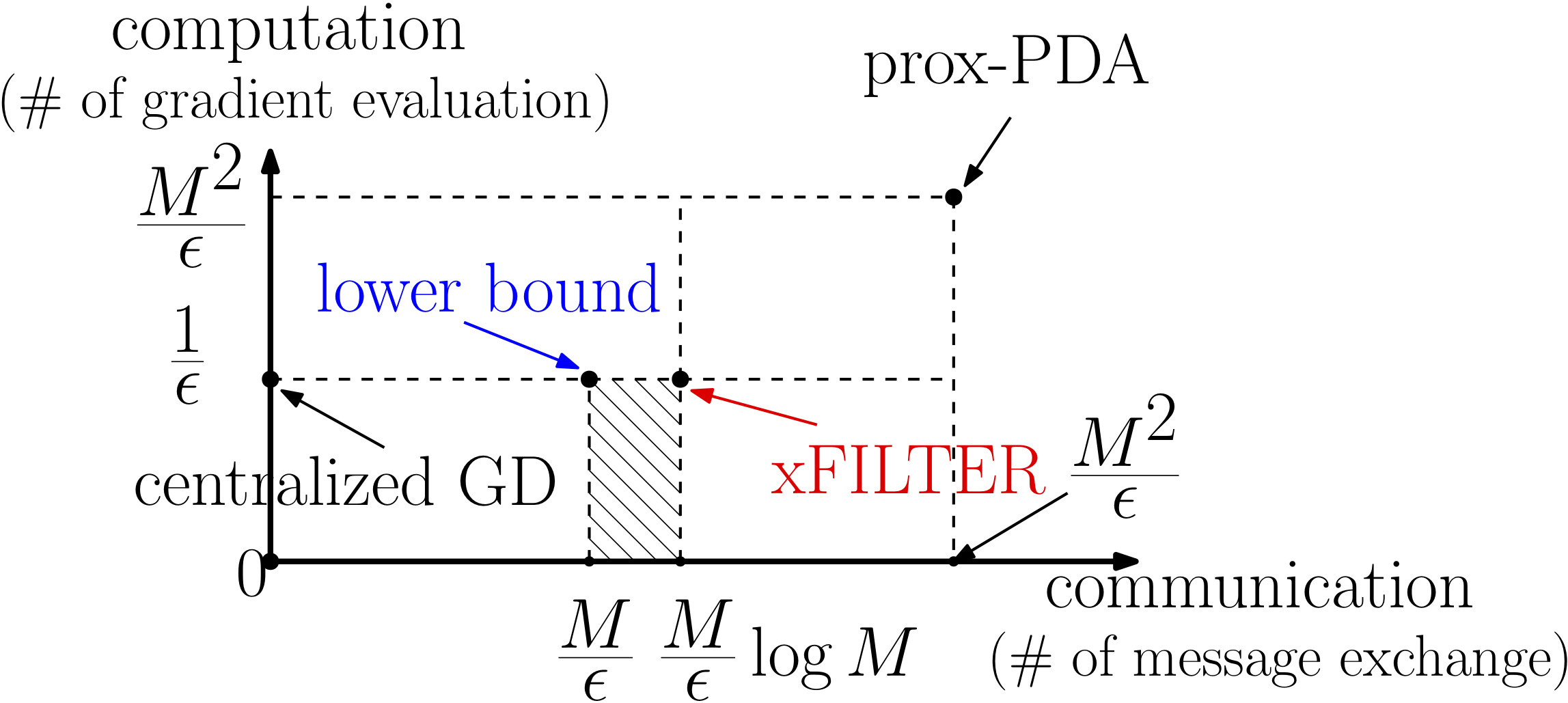 |
This paper discusses the fundamental performance for distributed non-convex optimization, where multiple nodes collectively optimize some non-convex function using local data. For a class of non-convex problems, we develop an “optimal” distributed algorithm called xFILTER, in the sense that it achieves the best possible convergence rate for a class of first-order distributed algorithms. In the left figure, we illustrate the results derived in this paper (both the lower bound and xFILTER bound), by comparing them with the rates of an non-optimal D-GPDA method, and the centralized gradient descent (GD) methods (over a path graph with M nodes, to achieve certain A short version of this paper won the Best Student Paper Award in 52nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers (Asilomar), October 2018. available at [IEEE Xplore]. |
Haoran Sun, Xiangyi Chen, Qingjiang Shi, Mingyi Hong, Xiao Fu and Nikos D. Sidiropoulos, “Learning to Optimize: Training Deep Neural Networks for Wireless Resource Management”, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 66.20 (2018): 5438-5453; available at [IEEE Xplore] [arXiv] [code].
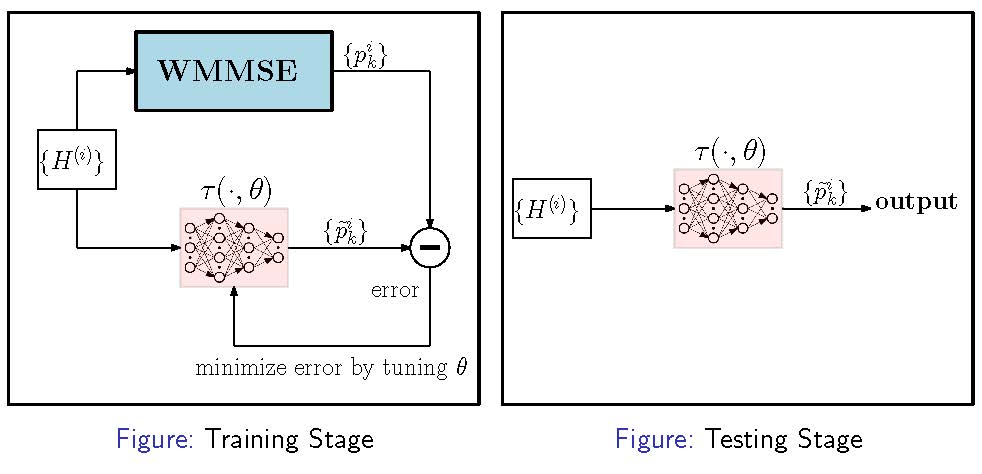 |
This paper address both the theoretical and practical aspects of deep learning based algorithm approximation with applications to wireless resource management. The key idea is to treat the input and output of an SP algorithm as an unknown nonlinear mapping and use a deep neural network (DNN) to approximate it. If the nonlinear mapping can be learned accurately by a DNN of moderate size, then SP tasks can be performed effectively — since passing the input through a DNN only requires a small number of simple operations. Prof. Nikos Sidiropoulos (ECE at University of Virginia) gave a Keynote at ICC Workshop ‘‘Machine Learning for Communications’’ about this paper. See the slides here. The IEEE Communications Society (ComSoc) has provided a list of papers for “Best Readings in Machine Learning in Communications”. This paper is included in this list for ‘‘Resource Allocation’’. |
 )
) 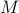 . To maintain the good performance over all experienced data from
. To maintain the good performance over all experienced data from 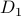 to
to 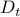 , the proposed framework optimizes the data-driven model at each time
, the proposed framework optimizes the data-driven model at each time 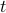 , based on the mixture of the current data
, based on the mixture of the current data  -solution). The xFILTER can significantly reduce both # of gradient evaluations, and # of communication rounds among the distributed nodes.
-solution). The xFILTER can significantly reduce both # of gradient evaluations, and # of communication rounds among the distributed nodes.